Gum Disease
Raleigh, NC
Gum Disease Treatment provided by Dr. Neill
and Dr. Lee
in Raleigh, NC at Raleigh Family Orthodontics
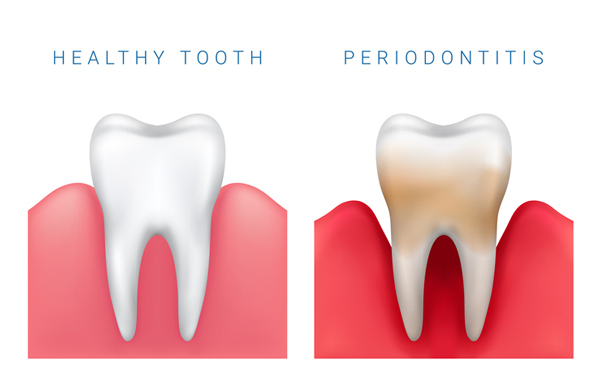 Gum disease is a common but serious condition that affects millions of people everyday. What we call gum disease is actually an umbrella term for all of the diseases that affect the tissues surrounding the teeth. Also known as periodontal disease, these conditions range from gingivitis that is only a mild inflammation of the gums, to severe periodontitis that causes tooth loss. Gum disease is a common but serious condition that affects millions of people everyday. What we call gum disease is actually an umbrella term for all of the diseases that affect the tissues surrounding the teeth. Also known as periodontal disease, these conditions range from gingivitis that is only a mild inflammation of the gums, to severe periodontitis that causes tooth loss.
Great oral hygiene and regular dental check ups are crucial to prevent and manage gum disease. Without brushing at least twice per day, flossing daily, and attending professional teeth cleanings and checkups, gum disease is allowed to develop and progress. It negatively affects oral health, but left unchecked, gum disease can also contribute to systemic conditions such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
What is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal gum disease begins when dental plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, accumulates on the teeth. This plaque consumes sugars and starches from food, and produces acids that irritate the gums and erode tooth enamel. If dental plaque is not removed through proper oral hygiene and professional cleanings, it hardens into tartar. Tartar is much more difficult to remove from the teeth, and leads to gum inflammation, infection and tooth loss.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the earliest, mildest form of gum disease. It is characterized by red, swollen gums that bleed easily while brushing and flossing. Gingivitis is often painless, so it is overlooked. However, with proper dental care, it is a reversible condition. Consistent brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar, and allow the gums to heal from gingivitis.
Periodontitis
When gingivitis is left untreated, it progresses into periodontitis. This is a more severe form of gum disease. With full blown periodontitis, the inner layer of the gums and jawbone pull away from the teeth. Then infected pockets form in that area between the jaw and teeth. The body's immune system fights the bacteria, but without treatment, the plaque continues to grow below the gum line. The acids produced by the bacteria and the body's response to the infection break down the bone and connective tissue that hold teeth in place. When gum disease goes unchecked for long enough, the bone, gums, and the tissue that supports the teeth are destroyed, and teeth are lost.
Risk Factors for Gum Disease
Several factors increase the risk of gum disease development. Poor oral hygiene is the most significant factor because it allows plaque to build up and harden into tartar. Another huge factor for gum disease is smoking, which impairs gum tissue and reduces blood flow to the gums, which makes the gums more susceptible to infection. Hormonal changes in women, such as those occurring during pregnancy or menopause, can also make gums more sensitive and susceptible to gingivitis. Some of our patients are more susceptible to gum disease because of genetics.
In addition, illnesses such as diabetes can affect the condition of the gums. Diabetes reduces the body's resistance to infection. Medications that cause dry mouth, such as some antihistamines, decongestants, painkillers, and antidepressants, also increase the risk of gum disease because saliva protects the mouth and gums.
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
Recognition of the signs and symptoms of gum disease are crucial for early intervention. Common signs include persistent bad breath, swollen gums, tender gums, bleeding gums, painful chewing, loose or sensitive teeth, and receding gums. When the gums recede, the teeth appear longer. If you experience any of these symptoms, please seek professional dental care immediately.
Prevention and Management
Preventing gum disease begins with good oral hygiene. We recommend that patients brush their teeth at least twice per day, and floss at least once per day before bedtime. Great oral hygiene practices remove plaque, and prevent tartar that causes gum disease. Regular dental check ups and professional cleanings are also crucial to maintain oral health. Our team can remove tartar that cannot be eliminated by brushing and flossing alone, and we can act quickly when there are early signs of gum disease.
Treatment
For patients diagnosed with gum disease, management focuses on controlling the infection. The appropriate treatment is dependent on the severity of the disease. In the early stages, treatments such as scaling and root planing, which clean the root surfaces of the teeth, are effective. This procedure removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line, and smooths the root surfaces to discourage further bacteria growth.
In severe cases, surgical treatments may be necessary. These include flap surgery, where the gums are lifted back to remove tartar deep below the gum line, and bone and tissue grafts, which help regenerate bone or gum tissue destroyed by periodontitis. Antibiotics may be prescribed to control infection.
The Impact of Gum Disease on Overall Health
Research has shown that gum disease has negative effects on our bodies outside of oral health. Studies have linked periodontal disease to systemic conditions including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. The gum inflammation from periodontal disease contributes to the development of these conditions.
For example, patients with periodontal disease are at a higher risk of heart disease. The bacteria from infected gums can enter the bloodstream and attach to the fatty deposits in the arteries, which leads to the formation of blood clots, and increased risk of heart attacks. In addition, patients with diabetes are more susceptible to gum infections. Gum disease worsens diabetes, and diabetes worsens gum disease in a terrible cycle.
The Importance of Education
Educating our patients about gum disease is essential to prevention, as well as early treatment. Many of our patients do not realize that they have gum disease until it has done a significant amount of damage. Everyday, we hope to educate our patients about the importance of oral hygiene and regular dental visits.
Gum disease is prevalent and serious. It leads to significant oral health issues, and when it contributes to heart disease and diabetes, negatively impacts our health overall. Through proper oral hygiene, regular dental visits, and education, gum disease can be prevented and managed effectively. Early detection and treatment are key to maintaining healthy gums, and a healthy body that is free of gum disease and all that it affects. |
